Arrow cards
Each pupil has a set of Arrow cards.Pupils combine their arrow cards to make numbers.
Play ‘Show me’ activities and ask questions about place value such as:
Show me 38 470; 52 000; 17 906; ... . Which cards did you use?
Show me a number which has 1; 4; 6; ... in the thousands column.
Include multiplying numbers by 10, 100 and 1000:
Show me 42; 50; 607; 348; ... multiplied by 10.
Show me 16; 25; 30; 506; 750; ... multiplied by 100.
Show me 6; 13; 43; 60; 81; ... multiplied by 1000.
Extend to dividing by 10, 100 and 1000:
Show me 80; 560; 700; 11 000; ... divided by 10.
Show me 600; 9000; 170 000; ... divided by 100.
Show me 3000; 14 000; 32 000; ... divided by 1000.
Discuss ways of checking how many zeros the answer will have.
Elastic-band strips
Each pupil will need an unmarked strip of card on which is stretched and elastic band. The strips should be of different lengths.Tell pupils that one end of the strip is zero and the other end is 1000.
Ask them to slide the band along the strip to show the approximate position of 500. They then hold the strips up to show their estimations.
Repeat for different numbers between 0 and 1000 such as 250, 460, 538, 896, ...
Discuss how the positions on the strip are approximate.
Change the values at each end of the strip to zero and 10 000 and repeat the activity.
Mental numbers
Pupils sit with their eyes closed and imagine a number written on the inside of their eyelids.
Imagine this number to be 48652.
Which number is on the left? Which is on the right?
Which digit is in the thousands column? Which digit is in the tens column?
Change over the positions of the 6 and 2. What is the new number?
Make the number one more. What is it now?
Now make this number ten more. What is the new number?
Subtract 100 from the number. What is the number now?
Change the starting number.
Number beginnings
Discuss ways in which we can work out the values of and relationships between numbers by looking at the beginning of words. For insance: penta, deci, centi, milli, kilo, ...
Extend to number beginnings such as mega and giga. Giga is often used in computing for very large numbers, such as gigabyte. It stands for a thousand million.
Talk about large numbers, such as millions, billions and trillions. Explain how a new word, googol, has been made up to describe 1 followed by a hundred zeros.
Digit cards
Use Digit cards 0-9.
Pupils draw four boxes in which to write the digits to make a number with two decimal places. They write a decimal point in the correct place between the boxes.
Shuffle the digit cards and choose a card at random. Show it to the pupils and ask them to choose in which of the four boxes to write the digit. The aim is to write digits in the boxes to match a target.
Targets
The largest/smallest number.
The number nearest to 40.
A number that rounds to 35.5
A number that rounds to 60
Extend the activities to use thousandths.
My number is...
A pupil thinks of a decimal number. The others take turns to ask a question about it which can only be answered yes or no.
Is your number between 2 and 5? Yes.
Does your number have tenths and hundredths? Yes.
Does your number round to 3 to the nearest whole number? No.
Is the tenths digit larger than the hundredths digit? Yes.
This continues until someone guesses the number, then that pupil ‘thinks of a number’.
Comparing numbers
Introduce the symbols > (is greater than) and < (is less than).
Write on the board 21.34 ![]() 23.14 and ask for the sign.
23.14 and ask for the sign.
Repeat with other pairs of numbers.
Write 61.49 < ![]() < 61.72 on the board.
< 61.72 on the board.
Which numbers could it be?
Compare other numbers in this way, putting a list of decimal numbers in order.
Rounding
Explain the rules for rounding numbers. Pupils use arrow cards and a decimal point to show the answer.
Show me 12.6, 2.54, 8.78, ... rounded to the nearest whole number.
Show me 11.22, 68.42, 35.86, ... rounded to the nearest tenth.
Calculator constants
Organisation: groups or pairs
Pupils take turns to use the constant x10 by inputting 10xx = and another input, such as 0.45. The partner predicts what the display will show each time the equals key is pressed. This can be repeated for the constant x100, and for ÷10 and ÷100.
Counting stick
Use a counting stick and call one end of the stick zero and the other end 1.· Point to each division in turn and ask for the appropriate decimal number.
· Point to random positions and ask for the appropriate decimal numbers.
· If pupils are confident with this activity point to the mid points between the divisions to generate decimal numbers such as 0.75, 0.45, 0.85, ...
Washing lines
Use a short length of washing line to which pupils clip numbers using small bulldog clips or clothes pegs.Clip a decimal point to the line and decide upon the range of decimal numbers to use.
Start with a decimal number such as 2.75, then ask pupils to:
Make it ten more.
Divide it by 10.
Add 0.01 to it.
Halve it.
Include:
· Multiplying and dividing by 10, 100, ...
· Increasing and decreasing by 10, 100, ...
Decimal arrow cards
Each pupil has set of Decimal arrow cards.Pupil combine their Arrow cards to make decimal numbers.
· Play ‘Show me’ activities asking questions about place value, such as:
Show me 0.75; 3.25; 4.125; ... . Which cards did you use?
Show me a number which has 2; 5; 9; ... in the tenths column.
Show me a number which has 1; 0; 4; ... in the hundredths column.
Increase your number by 0.1; 0.5; 0.01; ...
Decrease your number by 0.2; 0.6; 0.03; ...
· Pupils work in cooperating groups, each member making a different decimal number. The group cooperates to show:
The largest decimal number in the group
The smallest number in the group
The number nearest to 1; 0.5; 0.75; ...
Elastic-band strips
Pupils use strips of scrap card which they divide into ten sections. The bottom left corner of their strips should be marked to show them where to hold it (or bottom right corner for left-handed pupils).Each strip should have an elastic band on it, sufficiently tight that it can be moved along the strip without dropping off. The strips need not all be the same size.
Tell pupils that one end of the strip is zero and the other end is 1.
· Ask them to slide the band along the strip to show the approximate position of 0.5. They then hold the strips up to show their estimations.
· Repeat for different numbers between 0 and 1 such as 0.7; 0.2; 0.9; ...
· Extend to showing decimals such as 0.75; 0.15; 0.05; ...
· Discuss rounding decimals, then ask pupils to show 0.524; 0.682; 0.304; ...
Discuss how the positions on the strip are approximate.
Extend the activity using different lengths of unmarked strips.
Repeat the activities with pupils showing their estimations and approximations.
Pupils can swap their strips with each other so that they use different lengths of card.
To help them count, the Romans placed pebbles in columns.
They called these pebbles calculi.
Look at these numbers. A pebble above the bar stands for 5.
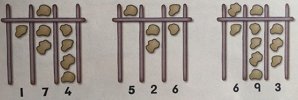
Use 5 counters and arrange them in a frame like this.

- What is the largest number you can make?
- What is the smallest number?
- Which is the nearest number to 500 you can make?